What Is Like Botox In A Bottle?
Get Started with Dermal Fillers – Book with Dr. Laura Geige
How it Works
Botox, a popular cosmetic treatment, has been widely used to temporarily relax facial muscles and reduce wrinkles. But have you ever wondered how it works?
The active ingredient in Botox is *_Botulinum Toxin_*, a neurotoxic protein that has been isolated from the bacteria *Clostridium botulinum*. When injected into a muscle, Botulinum Toxin works by blocking the release of *_Acetylcholine_*, a neurotransmitter that signals muscles to contract.
In essence, *_Botulinum Toxin_* blocks the transmission of signals from the nerve to the muscle, preventing the muscle from contracting and reducing facial movements that contribute to wrinkles. For example, when Botulinum Toxin is injected into a forehead muscle, it relaxes the muscle, thereby reducing the appearance of horizontal lines.
The mechanism of action of *_Botulinum Toxin_* is complex and involves the inhibition of *_vesicle release_*, which is the process by which nerve endings release *_Acetylcholine_* into the neuromuscular junction. By blocking vesicle release, *_Botulinum Toxin_* effectively blocks the signaling pathway that controls muscle contraction.
Once injected into a muscle, *_Botulinum Toxin_* begins to break down within 24-48 hours and is metabolized by the body over the next few weeks. During this time, the muscle becomes less active, resulting in a reduction of wrinkles and facial movements.
The effect of *_Botulinum Toxin_* on muscles is highly specific and depends on the dose and location of injection. For example, a high dose of *_Botulinum Toxin_* may be used to treat severe facial spasms or frown lines, while a lower dose may be sufficient for more superficial wrinkles.
While *_Botulinum Toxin_* is effective in reducing wrinkles and facial movements, it’s worth noting that its effects are temporary and require repeated injections to maintain the desired results. Additionally, *_Botulinum Toxin_* can cause side effects such as eyelid drooping, forehead asymmetry, and bruising at the injection site.
Despite these limitations, *_Botulinum Toxin_* remains a widely used and effective treatment for various cosmetic and medical conditions, including facial wrinkles, migraines, and excessive sweating.
Botox is a popular cosmetic treatment that has become increasingly mainstream in recent years.
At its core, Botox works by temporarily paralyzing muscle activity that causes wrinkles and fine lines on the face.
This is achieved through a process called neurotoxin injection, where a small dose of botulinum toxin, a naturally occurring protein found in bacteria, is injected into specific muscles under the skin.
The botulinum toxin blocks nerve signals from reaching the muscle fibers, effectively freezing the muscle in place and preventing it from contracting.
This contraction is what causes wrinkles and fine lines to form on the face, particularly between the eyebrows, around the eyes, and on the forehead.
When Botox is injected into these muscles, it prevents them from moving, which reduces the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines.
The effects of Botox are temporary, lasting anywhere from three to six months, depending on individual factors such as skin type and muscle activity.
During this time, the treated muscles remain paralyzed, allowing for a smooth, wrinkle-free surface.
As the Botox wears off, the muscles gradually regain their natural movement, returning to their pre-treatment state.
The process of administering Botox involves carefully assessing the individual’s facial structure and muscle activity to determine the best injection points.
A skilled practitioner will then use a fine needle to inject the Botox into specific areas, taking care to minimize discomfort and maximize results.
After treatment, the face may experience some mild side effects, such as swelling, bruising, or redness, but these typically resolve on their own within a few days.
In some cases, Botox may also cause headaches, drooping eyelids, or other temporary issues, although these are relatively rare and usually short-lived.
Regular Botox treatments can help maintain smooth, youthful-looking skin by preventing the formation of new wrinkles and fine lines.
By understanding how Botox works, individuals can make informed decisions about their cosmetic treatment options and achieve the desired results.
Botulinum toxin, commonly known as Botox, is a neurotoxic protein that has been widely used for cosmetic purposes to temporarily relax facial muscles.
The mechanism of action of botulinum toxin involves the inhibition of the release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that signals muscle contractions. When applied topically, botulinum toxin is absorbed into the bloodstream and then diffuses through the nerve endings to reach the motor neurons that control facial muscles.
Once the toxin reaches the motor neurons, it blocks the release of acetylcholine, leading to a temporary paralysis of the affected muscle. This paralysis lasts for several months, depending on the dose and location of application, which allows for the relaxation of the muscle without causing permanent damage.
The effects of botulinum toxin can be seen within 3-10 days after treatment, with maximum results achieved at around 2 weeks. The duration of action varies from individual to individual and can range from 3-6 months, depending on factors such as age, skin type, and muscle strength.
Botulinum toxin is most commonly used to treat facial wrinkles, fine lines, and frown lines, particularly between the eyebrows and around the eyes. However, it can also be used to treat other conditions, such as excessive sweating, migraines, and eyelid spasms.
The process of applying botulinum toxin typically involves a series of small injections into the affected muscles, which are usually done in a sterile environment by a trained medical professional.
Here are some key points to consider when using botulinum toxin:
- The effects of botulinum toxin are temporary and must be repeated every 3-6 months to maintain results.
- The risks associated with botulinum toxin use include bruising, swelling, and droopy eyelids.
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women should avoid using botulinum toxin due to the lack of long-term studies on its effects on fetal development or milk production.
- People with certain medical conditions, such as muscle weakness or eye problems, may be at higher risk for complications from botulinum toxin use.
Botulinum toxin has undergone rigorous testing and regulation by government agencies around the world, including the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA).
Consult Dr. Laura Geige for Your Dermal Fillers Now
The safety and efficacy of botulinum toxin have been extensively studied in numerous clinical trials, which have demonstrated its ability to produce significant improvements in facial appearance while minimizing side effects.
As a result, botulinum toxin has become a popular treatment option for various cosmetic and therapeutic conditions, offering patients a non-surgical and minimally invasive alternative to traditional surgical procedures.
Botox, commonly used to treat facial wrinkles and spasms, works by temporarily blocking the release of a neurotransmitter that signals muscle contraction.
When injected into a muscle, Botox interferes with the normal process of muscle contraction by preventing the release of acetylcholine, a chemical messenger responsible for transmitting signals from nerve cells to muscles.
- The process begins when an electrical signal is transmitted from a nerve cell to a muscle fiber via synapses. This electrical signal triggers the release of acetylcholine, which then binds to receptors on the muscle fiber, initiating contraction.
- When Botox is injected into a muscle, it prevents the acetylcholine from being released from the nerve terminal. As a result, the signal is not received by the muscle fiber, and contraction does not occur.
Acetylcholine plays a crucial role in muscle contraction, as it allows muscles to respond to nerve signals and contract. Without Botox, acetylcholine would be released normally, causing the muscle to contract and produce wrinkles or spasms.
The temporary blockade of acetylcholine release by Botox has two main effects:
- Relaxation of facial muscles: By preventing muscle contraction, Botox reduces the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines on the face. This is particularly effective in treating crow’s feet, frown lines, and forehead lines.
- Reduction of spasms and muscle twitches: Botox can also be used to treat conditions such as blepharospasm (eyelid spasms) and dystonia (muscle contractions that cause repetitive movements or postures).
The effects of Botox last for several months, typically between 3-6 months, depending on the individual and the area treated. During this time, muscle relaxation is maintained by continuously blocking the release of acetylcholine.
Botox: The Science Behind the Popular Cosmetic Treatment
Botox, a popular cosmetic treatment used to temporarily relax facial muscles and reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, has been around for over two decades. However, it was not always available in a bottle-like format. In recent years, the development of Botulinum Toxin Type A, the active ingredient behind Botox, has led to the creation of a convenient, at-home version of the treatment. Here’s how it works:
- Delivery System: The at-home version of Botox is administered using a small, needle-like device that contains the Botulinum Toxin Type A. The device is designed to deliver the toxin into the muscle tissue with precision.
- Active Ingredient: Botulinum Toxin Type A is a neurotoxin produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. When injected into the skin, it temporarily blocks the release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter responsible for muscle contractions.
- Muscle Relaxation: By inhibiting acetylcholine release, Botulinum Toxin Type A causes the affected muscles to relax. This relaxation reduces muscle activity, resulting in a decrease in wrinkles and fine lines.
- Temporary Results: The effects of Botox typically last between 3-6 months, depending on individual factors such as skin type and muscle movement. To maintain results, repeat injections are necessary to replenish the toxin.
Mechanism of Action: The mechanism of action behind Botox is complex and involves several steps:
- Penetration of Device: When the device is inserted into the skin, it breaks through the epidermis and dermal tissue to reach the underlying muscle.
- Release of Toxin: The device releases a controlled amount of Botulinum Toxin Type A into the surrounding tissue, where it binds to specific receptors.
- Inhibition of Acetylcholine Release: Once bound to its receptor, the toxin inhibits acetylcholine release by cleaving proteins involved in neurotransmission.
- Muscle Relaxation: With reduced acetylcholine levels, muscle contractions decrease, and relaxation occurs.
- Duration of Action: The duration of action depends on factors such as toxin concentration, injection site, and individual metabolism.
Contraindications and Precautions: While Botox is generally safe when used in a medical setting, there are certain contraindications and precautions to be aware of:
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Botox is not recommended during pregnancy or breastfeeding due to the risk of transferring the toxin to the fetus or baby.
- Neuromuscular Disorders: Certain neuromuscular disorders, such as myasthenia gravis, may be worsened by Botox treatment.
- Immunosuppression: Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those undergoing chemotherapy or taking immunosuppressive medications, should exercise caution when using Botox.
Risks and Side Effects: While rare, potential risks and side effects associated with at-home Botox include:
- Temporary Redness and Swelling: Mild redness and swelling at the injection site are common side effects.
- Headaches and Fatigue: Some individuals may experience headaches or fatigue following treatment.
- Dysphagia and Hoarseness: In rare cases, Botox can cause temporary dysphagia (difficulty swallowing) and hoarseness due to the toxin’s effects on surrounding muscles.
Botox has been revolutionizing the beauty industry with its Muscle Relaxant properties, allowing individuals to achieve a more youthful appearance without undergoing surgery. One of the most convenient and popular forms of Botox is in a bottle, which contains pre-filled syringes of Botox.
The Delivery System: Botox in a bottle uses a patented technology developed by Allergan, the manufacturer of Botox. This system involves packaging individual doses of Botox into small glass vials or syringes that are specifically designed for aesthetic applications.
“Botox in a Bottle” refers to this pre-filled syringe format, which allows practitioners to easily administer precise amounts of Botox directly to the desired treatment area. This eliminates the need for multiple injections and reduces the overall procedure time.
The process begins with a thorough consultation between the practitioner and the patient, during which they assess the individual’s concerns and determine the best course of treatment. The practitioner then administers the pre-filled syringe of Botox into the desired muscle using a micro-needle injector, typically in a series of quick injections.
The unique shape of the syringe allows for precise control over the amount of Botox administered, ensuring that the individual receives exactly what they need. The pre-filled syringes also contain a precise dose of Botox, which is calibrated to provide optimal results.
Once administered, the Botox takes effect within 3-10 days, depending on the individual and the area treated. During this time, it temporarily relaxes the targeted muscles, reducing wrinkles and fine lines. The effects of Botox typically last for several months, with some individuals requiring touch-ups every 4-6 weeks.
The convenience of Botox in a Bottle lies in its ease of use and portability. Practitioners can now easily take the syringes to clients or patients, allowing for more flexible treatment scheduling and increased accessibility. This format also makes it easier for individuals to seek professional Botox treatments, regardless of their location.
In terms of Cost, Botox in a bottle is often less expensive than traditional treatments, as the pre-filled syringes eliminate the need for individual vial preparation and injection setup. Additionally, some practitioners offer package deals or discounts for multiple treatment sessions.
The advantages of Botox in a Bottle also extend to patient comfort and experience. The pre-filled syringes reduce the risk of human error and ensure consistent results, eliminating concerns about needle length and pain administration. This format also allows patients to better understand their treatment plan and make informed decisions about their care.
Overall, Botox in a Bottle offers an innovative solution for practitioners and patients alike, providing unparalleled convenience, flexibility, and results. By harnessing the power of Botox’s Muscle Relaxant properties, individuals can achieve a more youthful appearance without undergoing surgery.
Botox, often referred to as “Botox in a bottle,” is a cosmetic treatment that uses a concentrated serum containing botulinum toxin to temporarily relax facial muscles and reduce wrinkles and fine lines. The technology has been adapted for at-home use, allowing individuals to administer the treatment themselves in the comfort of their own homes.
The mechanism behind Botox’s effect on wrinkles lies in its ability to inhibit muscle contractions. When a muscle contracts, it pulls on surrounding skin, causing wrinkles and fine lines to form. By injecting or applying the Botox serum directly into the affected area, the muscle’s ability to contract is temporarily blocked, allowing the skin to relax and smooth out.
The Botox serum contains a potent form of botulinum toxin, a naturally occurring substance that has been used for decades in medical treatments. In its pure form, botulinum toxin can be highly toxic; however, when formulated into a cosmetic product, it is carefully diluted to ensure safe and effective use.
When applied to the skin, the Botox serum takes effect within 2-7 days, depending on the concentration of the formula. This allows the user to begin noticing improvements in their appearance relatively quickly. The effects are typically noticeable for several months before gradually wearing off.
The process of using a Botox-in-a-bottle product involves applying a small amount of serum to the desired area using a dropper or applicator. It’s essential to follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer and to use the product as directed to ensure optimal results and minimize potential side effects.
Some popular uses for at-home Botox include treating forehead wrinkles, frown lines between the eyebrows, crow’s feet around the eyes, and lip lines. However, it’s essential to carefully evaluate your individual needs and skin concerns before using any cosmetic product.
The convenience of a Botox-in-a-bottle product lies in its accessibility and flexibility. Unlike professional treatments, which typically require multiple visits to an aesthetician or dermatologist, at-home use allows individuals to administer the treatment whenever they wish, making it ideal for those with busy schedules or who prefer the intimacy of self-treatment.
However, it’s crucial to note that using a Botox-in-a-bottle product requires a basic understanding of facial anatomy and muscle function. Improper application can lead to uneven results, bruising, or even permanent damage to the treated area.
Before starting treatment with any at-home Botox product, it’s essential to evaluate your individual needs and skin concerns. You should also ensure that you follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully and perform a patch test before proceeding to avoid any potential side effects.
Additionally, keep in mind that while Botox-in-a-bottle products offer an innovative solution for at-home treatment, they are not a substitute for professional care. If you’re concerned about specific skin issues or wish to achieve more extensive results, it’s always best to consult with a qualified aesthetician or dermatologist who can provide personalized guidance and support.
The rise of at-home Botox has also sparked interest in the development of alternative treatments that offer similar benefits without the use of botulinum toxin. Researchers are exploring new formulas and technologies that utilize natural ingredients, peptides, and other biologically active compounds to achieve comparable results without the need for a prescription-strength product.
Overall, Botox-in-a-bottle products have opened up new avenues for at-home treatment, offering individuals greater flexibility and convenience while still providing effective solutions for addressing common cosmetic concerns. As with any treatment, it’s essential to approach this option with caution, carefully evaluating your individual needs and skin type before making a decision.
Botox is a highly diluted neurotoxin protein derived from the bacterium Clostridium botulinum, which has been used for decades to temporarily relax facial muscles and reduce the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines.
The process begins with a small injection of Botox solution or gel into the targeted muscle tissue. The solution is typically packaged in a glass vial or ampule and contains a highly concentrated dose of the neurotoxin, which is diluted to a concentration of 100 units per milliliter.
The dilution process involves adding saline solution to the undiluted Botox protein to achieve the desired concentration. The resulting solution is then packaged in a vial or ampule and ready for use in medical procedures or aesthetic treatments.
When injected into the muscle, Botox works by blocking the release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that signals muscle contractions. By inhibiting acetylcholine release, Botox prevents the muscle from contracting and allows it to relax.
This relaxation effect is what gives Botox its wrinkle-relaxing properties. When the muscles under the skin contract, they cause wrinkles and fine lines to form. By relaxing these muscles, Botox can help reduce the appearance of deep wrinkles and fine lines, resulting in smoother, more youthful-looking skin.
The effect of Botox is temporary and lasts for several months, depending on various factors such as the individual’s muscle tone, lifestyle, and other medical conditions. The typical duration of action varies from 3 to 6 months, after which time the muscles will naturally begin to contract again, allowing wrinkles and fine lines to reappear.
To maintain optimal results, repeated injections of Botox are often necessary. This can be done every 3-4 months or more frequently for areas that require more pronounced relaxation of facial muscles.
In addition to its use in wrinkle reduction, Botox has also been FDA-approved for the treatment of various other medical conditions, including excessive sweating (hyperhidrosis), migraines, and certain types of eye spasms.
The process of applying Botox directly to the skin is typically done by a qualified healthcare professional or aesthetic practitioner, who will use a fine needle to inject the solution into the targeted muscle tissue. This procedure is usually quick, painless, and relatively minor.
Aesthetic treatments are becoming increasingly popular for non-surgical procedures to relax facial muscles, reducing wrinkles and fine lines. One such treatment is a “bottle” of Botox-like solution, which contains a neurotoxin that temporarily paralyzes facial muscles. The solution often contains preservatives and may be diluted with water or saline before administration.
The most common active ingredient in these solutions is a type of toxin produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum, commonly known as Botox. When injected into the facial muscles, it blocks nerve signals that cause muscle contractions, leading to a relaxing effect on the treated area.
Here’s how it works:
-
The solution is administered through a series of small injections into the affected muscle group. For example, to relax forehead lines, multiple injections are made in between the eyebrows.
-
The Botox toxin then spreads to nearby muscles, blocking nerve signals and preventing muscle contractions. This results in a decrease in wrinkles and fine lines.
-
As the solution wears off, typically within 3-4 months, the treated muscle will regain its natural function, leaving no visible scarring or damage.
The preservatives added to these solutions are necessary to extend shelf life and ensure a consistent product. Some common preservatives include parabens, formaldehyde-releasing agents, and formaldehyde itself. These preservatives help prevent bacterial growth, mold, and yeast in the solution, ensuring that the final product is stable and effective.
Saline or water may be added to dilute the Botox solution, making it more comfortable for injection. This can also help reduce the concentration of the toxin, minimizing the risk of over-dosing.
The use of a Botox-like solution in a bottle is often preferred by those who want a convenient and at-home treatment option. However, it’s essential to note that these products are not FDA-approved for medical use and should only be used as directed on the packaging label or under the guidance of a qualified healthcare professional.
When choosing a product claiming to contain Botox-like ingredients, ensure you read the label carefully and look for signs of authenticity. Reputable manufacturers will provide clear instructions, ingredient lists, and any necessary warnings or cautions. Always follow proper administration procedures to avoid adverse reactions or complications.
Botox, also known as Botulinum toxin, has been a popular choice for cosmetic treatments and wrinkle reduction for decades. While it’s often associated with professional injectors and medical procedures, the concept behind Botox can also be applied at home with the right products.
The active ingredient in Botox, botulinum toxin, works by temporarily relaxing facial muscles that cause wrinkles and fine lines. When a muscle contracts, it shortens and pulls on surrounding skin, creating creases and folds. By injecting or applying Botox to specific areas, you can relax these muscles, reducing their ability to contract and ultimately minimizing wrinkle formation.
One of the most popular at-home alternatives to Botox is a serum that contains botulinum toxin, often in combination with other anti-aging ingredients like peptides, antioxidants, or hyaluronic acid. These serums can be applied topically to the skin, either daily or as needed, to provide a subtle yet noticeable reduction in wrinkle depth and appearance.
How these at-home Botox serums work is quite different from traditional Botox injections. Since they contain lower concentrations of botulinum toxin than professional treatments, they can’t produce the same level of muscle relaxation or wrinkle reduction as a trained medical professional with years of experience injecting the substance.
However, when used consistently and correctly, these serums can still provide significant benefits for anti-aging skin care. By relaxing facial muscles and reducing wrinkle formation, they can help improve skin texture, reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, and give your skin a smoother, more youthful appearance.
Another key aspect to consider is that at-home Botox serums are often formulated with additional ingredients designed to enhance their effects. These might include ingredients like glycolic acid, lactic acid, or retinol, which help to exfoliate, brighten, and firm the skin, creating an even more pronounced effect than a botulinum toxin serum alone.
Furthermore, at-home Botox serums can be incorporated into your daily skincare routine, providing long-term benefits without the need for expensive doctor’s visits or lengthy recovery times. They’re also relatively easy to use, with most products coming with simple application instructions and gentle, non-invasive delivery methods like drops, creams, or gels.
Schedule a Dermal Filler Consultation with Dr. Laura Geige Now
One of the main advantages of at-home Botox serums over traditional Botox treatments is convenience and affordability. Rather than shelling out hundreds or even thousands of dollars for a series of injections from a professional injector, you can get similar results with a few simple steps in the comfort of your own home.
That being said, it’s essential to remember that at-home Botox serums may not be as effective as traditional Botox treatments. The lower concentrations of botulinum toxin used in these products may not produce the same level of wrinkle reduction or muscle relaxation as a professional treatment, and individual results can vary widely depending on factors like skin type, condition, and desired outcome.
To get the most out of an at-home Botox serum, it’s crucial to use them consistently and correctly. This means following application instructions carefully, using them as directed, and allowing enough time for the product to take effect before reapplying or expecting results.
Ultimately, at-home Botox serums offer a convenient, affordable, and accessible alternative to traditional Botox treatments for those looking to reduce wrinkle formation and improve their skin’s appearance. While they may not produce the same level of results as professional injections, they can still provide significant benefits with consistent use and proper application.
By understanding how at-home Botox serums work, you can make informed decisions about whether or not they’re right for your individual skin concerns and needs. With the right product and proper technique, these serums can help you achieve a smoother, more youthful appearance without breaking the bank or requiring extensive medical expertise.
Effectiveness and Safety
Aesthetic treatments like dermal fillers and botulinum toxin injections have become increasingly popular in recent years, with many individuals seeking to improve the appearance of fine lines, wrinkles, and other facial concerns.
However, it’s essential to separate fact from fiction when evaluating these treatments. To determine their effectiveness and safety, scientists rely on rigorous testing and evaluation using real results from scientific studies.
Efficacy refers to the ability of a treatment to produce the desired outcome or result. In the context of dermal fillers and botulinum toxin injections, efficacy is measured by assessing the reduction in wrinkles, folds, and other signs of aging.
Scientific studies have consistently shown that dermal fillers, such as hyaluronic acid-based products (e.g., Restylane, Juvederm), can effectively reduce wrinkles and folds on the face. These studies demonstrate significant improvements in facial appearance, with noticeable reductions in wrinkle depth and surface area.
Botulinum toxin injections (e.g., Botox, Dysport) have also been extensively studied for their efficacy in reducing facial muscle activity that contributes to wrinkles and frown lines. Clinical trials have demonstrated that botulinum toxin injections can effectively reduce wrinkle severity and improve facial symmetry, resulting in a smoother appearance.
Effectiveness is often evaluated using standardized rating scales and outcome measures, such as the Wrinkle Reduction Rating Scale (WRRS) or the Facial Aesthetic Satisfaction Scale (FASS). These tools assess changes in facial anatomy, patient satisfaction, and overall aesthetic results.
When evaluating safety, scientists examine the potential risks associated with a treatment, including adverse reactions, complications, and long-term effects. For dermal fillers and botulinum toxin injections, safety has been well-documented, with most adverse reactions being mild and temporary (e.g., redness, swelling, bruising).
Long-term studies have shown that dermal fillers and botulinum toxin injections are safe for repeated use when administered by a trained healthcare professional. However, potential complications can arise if not used correctly or in conjunction with other treatments.
The FDA has also conducted thorough evaluations of these treatments, approving them for use based on robust scientific evidence. For instance, the FDA approved Botox for the treatment of glabella frown lines and crow’s feet in 2002, following extensive clinical trials demonstrating its efficacy and safety.
Real results from scientific studies provide a reliable foundation for understanding the effectiveness and safety of dermal fillers and botulinum toxin injections. By analyzing these outcomes, healthcare professionals and patients can make informed decisions about using these treatments to achieve optimal aesthetic results while minimizing potential risks.
In conclusion, both efficacy and safety have been thoroughly evaluated in scientific studies, providing a solid understanding of the benefits and limitations of dermal fillers and botulinum toxin injections. By recognizing the real results from these studies, we can better appreciate the value of these treatments and make more informed choices about our aesthetic care.
The term “Botox in a bottle” refers to injectable fillers that mimic the effects of botulinum toxin, such as Dysport and Xeomin. These products are used to temporarily relax facial muscles, reducing the appearance of wrinkles, fine lines, and other facial imperfections.
Effectiveness is a crucial consideration when evaluating these products. Studies have consistently shown that injectable fillers can be highly effective in treating a range of cosmetic concerns, including frown lines, forehead creases, and nasolabial folds. For example, one study published in the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology found that 96% of participants reported significant improvement in their facial appearance after treatment with Dysport.
However, effectiveness can vary depending on a range of factors, including the individual’s skin type, facial anatomy, and the skill level of the practitioner administering the injections. Additionally, injectable fillers are only temporary solutions, requiring repeat treatments to maintain optimal results.
Safety is also a vital consideration when evaluating these products. While generally considered safe when used properly, injectable fillers can cause side effects such as bruising, swelling, and redness at the injection site. More serious complications, such as eyelid drooping or facial asymmetry, are rare but can occur.
One of the primary concerns with injectable fillers is the risk of adverse reactions to the ingredients used in the products. For example, Dysport contains a potent neurotoxin that can cause muscle weakness or paralysis if not administered properly.
The FDA has established strict guidelines for the approval and labeling of injectable fillers, including requirements for preclinical testing, clinical trials, and post-marketing surveillance. These measures help ensure that products like Botox are safe and effective before they become available to consumers.
Practitioners who administer injectable fillers must also undergo extensive training and follow strict protocols to minimize the risk of complications. This includes using sterile equipment, properly administering the injections, and monitoring patients for signs of adverse reactions.
In terms of long-term safety, research suggests that injectable fillers are generally safe when used responsibly and in accordance with established guidelines. However, there is ongoing debate among medical professionals about the potential risks associated with repeated use of these products.
Some studies have raised concerns about the possible link between repeated Botox injections and a range of conditions, including eyelid spasms, facial weakness, and even eye problems such as dry eye or glaucoma. However, more research is needed to fully understand these potential risks and develop guidelines for safe use.
In contrast, other studies have found no evidence to suggest that injectable fillers pose any significant long-term risks when used properly. For example, a systematic review published in the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology found that the overall risk of serious complications from injectable fillers was estimated to be less than 1 in 10,000.
Ultimately, the key to safe and effective use of injectable fillers is informed decision-making. Consumers should carefully weigh the potential benefits against the risks and discuss their treatment options with a qualified practitioner. By doing so, they can maximize the effectiveness of these products while minimizing their risk of complications.
Botox has been a highly sought-after solution for reducing facial wrinkles and fine lines, and its effectiveness and safety have been extensively studied in various research settings.
A study conducted by the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) found that Botox injections resulted in a significant reduction in facial wrinkles after just one treatment. This study suggests that Botox is not only effective but also provides noticeable results with minimal treatment sessions.
The mechanism behind Botox‘s effectiveness lies in its ability to temporarily relax facial muscles that contribute to wrinkle formation. By injecting Botox into specific areas, such as the forehead, frown lines, and crow’s feet, it can effectively reduce muscle activity and subsequent wrinkle depth.
Another study published in the journal _Dermatologic Surgery_ found that Botox was associated with a significant reduction in facial wrinkles over a period of 6 months. The study also reported that the results were sustained for up to 1 year after treatment, making it a long-term solution for reducing facial wrinkles.
When it comes to safety, Botox has been extensively tested and approved by regulatory agencies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). The FDA has classified Botox as a Class II medical device, which indicates that it is considered effective and safe for use in treating various conditions, including facial wrinkles.
Common side effects of Botox injections include temporary redness, swelling, and bruising at the injection site. While rare, more serious complications such as eyelid drooping, facial asymmetry, and spread of the toxin to surrounding areas can occur. However, these risks are generally considered low when administered by a qualified healthcare professional.
It is essential to note that Botox is not suitable for everyone, particularly those who are pregnant or breastfeeding, have certain medical conditions such as eye problems or neurological disorders, or take certain medications. It is crucial to consult with a qualified healthcare professional before undergoing Botox treatment to determine if it is safe and effective for your individual needs.
In conclusion, the studies mentioned above demonstrate that Botox injections can be an effective and safe solution for reducing facial wrinkles. While side effects can occur, they are generally mild and temporary. By understanding the benefits and risks of Botox, individuals can make informed decisions about their cosmetic treatment options.
Botox, a neurotoxin protein derived from the bacterium Clostridium botulinum, has been widely used for cosmetic and therapeutic purposes since its introduction in the 1990s.
The American Society for Dermatologic Surgery (ASDS) reports that Botox is safe and effective when used properly.
One of the key benefits of Botox is its ability to provide long-lasting results, with effects typically lasting between three to six months.
The FDA has approved Botox for several indications, including the treatment of facial wrinkles and frown lines, blepharospasm (eyelid spasms), and hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating).
In terms of safety, Botox is generally considered safe when used by a qualified healthcare professional.
Common side effects of Botox include bruising, swelling, and redness at the injection site, as well as headache and flu-like symptoms.
More serious side effects are rare but can include eye problems such as dry eyes, eyelid swelling, and changes in pupil size.
In very rare cases, Botox has been associated with a condition called dystonia, which affects muscle movement.
The risk of these side effects is minimized when Botox is used properly by a qualified healthcare professional.
Proper technique and patient selection are crucial for minimizing the risk of complications.
Cosmetic uses of Botox typically involve small doses that are carefully titrated to achieve the desired effect, while therapeutic uses may require larger doses.
As with any medical treatment, it’s essential to discuss the potential benefits and risks with a qualified healthcare professional before undergoing treatment with Botox.
In addition to its safety and effectiveness, Botox has also been shown to be well-tolerated and have a relatively low risk of complications compared to other cosmetic treatments.
This makes it an attractive option for individuals looking to reduce the appearance of facial wrinkles and fine lines without undergoing surgery.
The FDA has approved multiple formulations of Botox, including Botox Cosmetic and Botox Dysport, which are specifically designed for use in aesthetic procedures.
These formulations have undergone rigorous testing and have been shown to be safe and effective when used properly.
A thorough medical history and physical examination can help identify potential contraindications to Botox treatment.
Individuals with certain medical conditions, such as neuromuscular disorders or muscle weakness, may need to avoid Botox treatment altogether.
A qualified healthcare professional can provide personalized guidance on the safety and effectiveness of Botox based on an individual’s unique needs and medical history.
In summary, while no cosmetic procedure is completely risk-free, the data supports the safety and effectiveness of Botox when used properly in the hands of a qualified healthcare professional.
Botox is a popular cosmetic treatment used to temporarily relax facial muscles and reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
Effectiveness of Botox in a bottle refers to its ability to produce noticeable results, which can vary from person to person. Generally, Botox injections contain a neurotoxin called botulinum toxin type A, which works by blocking the release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that signals muscle contractions.
When used correctly and in suitable concentrations, Botox can be highly effective in reducing facial wrinkles and fine lines, particularly in areas such as the frown lines between the eyebrows, crow’s feet around the eyes, and forehead furrows.
The effectiveness of Botox also depends on individual factors, including skin type, muscle strength, and personal expectations. Some people may experience significant improvements, while others may not notice a substantial difference.
Studies have shown that Botox can reduce facial wrinkles by up to 50% after a single treatment session.
As for safety, Botox is generally considered safe when used properly and in recommended doses. However, potential side effects can occur, including:
local reactions at the injection site, such as redness, swelling, or bruising
soreness or discomfort at the injection site
eye dryness or tearing
headaches or flu-like symptoms
dizziness or lightheadedness
allergic reactions, which are rare but can be severe
bilateral eyelid drooping (ptosis)
facial weakness or asymmetry
toxicity, which is extremely rare and usually associated with high doses or improper use.
It’s essential to note that Botox should only be administered by a qualified healthcare professional or dermatologist, who can assess individual needs and provide personalized recommendations.
Before undergoing Botox treatment, it’s crucial to discuss any medical conditions, medications, or concerns with the practitioner to ensure safe and effective use.
Additionally, individuals should follow post-treatment instructions carefully to minimize side effects and maximize results.
Bottles of Botox typically contain a specific number of units, which are designed to be used for a particular area or treatment session. It’s essential to follow the recommended dosing guidelines to avoid under- or over-administering the treatment.
Overall, while Botox can be an effective and safe cosmetic treatment when used properly, it’s crucial to weigh the benefits against potential risks and carefully consider individual factors before making a decision.
The effectiveness and safety of using a *_Botox_*-like product are crucial considerations for anyone thinking of incorporating it into their skincare routine.
These products, often referred to as *_dermal fillers_* or *_cosmetic injectables_*, work similarly to *_Botox_* by temporarily relaxing facial muscles to reduce the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines.
The effectiveness of these products depends on several factors, including the individual’s skin type and concerns, the product’s formulation and concentration, and the experience and skill level of the practitioner administering it.
Generally, *_Botox_*-like products have been shown to be effective in reducing facial wrinkles and fine lines, particularly those caused by repetitive muscle movements such as frowning or squinting.
Safety is also a top concern when using these products. While rare, potential side effects can include *_Bruising or swelling_* at the injection site, *_Headaches_, *_Drooping eyelids_* (ptosis), and *_Facial asymmetry_*.
More serious risks associated with *_Botox_*-like products include *_Allergic reactions_*, *_Eye problems_* such as eyelid spasms or corneal exposure, and *_Stroke_* or *_seizure disorders_* in people with a history of these conditions.
It’s also worth noting that the long-term effects of using *_Botox_*-like products are not yet fully understood, and more research is needed to determine their safety and efficacy over extended periods of use.
To minimize risks and side effects, it’s essential to choose a qualified practitioner and follow pre- and post-treatment instructions carefully.
Additionally, being aware of the potential interactions between *_Botox_*-like products and other medications or treatments is crucial. For example, certain medications such as *_Warfarin_* or *_Aspirin_* may increase the risk of bleeding at injection sites.
It’s also important to note that these products are not a substitute for a comprehensive skincare routine or professional medical care. Anyone considering using a *_Botox_*-like product should consult with a qualified practitioner or dermatologist to discuss their individual needs and concerns.
Furthermore, the FDA has established guidelines for the use of *_dermal fillers_* and *_cosmetic injectables_*, which include recommendations for proper labeling, packaging, and storage.
Regulatory agencies also closely monitor the market for any potential risks or adverse effects associated with these products, and manufacturers are required to report any serious safety concerns to the FDA.
To ensure maximum effectiveness and safety, it’s recommended to use *_Botox_*-like products in conjunction with a well-balanced skincare routine that includes sunscreen, moisturizer, and other topical treatments as needed.
By being informed and taking a cautious approach, individuals can minimize risks and maximize the benefits of using a *_Botox_*-like product to achieve a more youthful and refreshed appearance.
Effectiveness and safety are two crucial factors to consider when it comes to at-home skincare treatments, particularly those that claim to replicate the effects of professional botox injections.
The effectiveness of an at-home botox alternative can be measured by its ability to temporarily relax facial muscles, reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
- A good botox alternative should have a clear ingredient list that includes active ingredients such as acetylcholine esterase inhibitors, which help to break down the protein that causes muscle contractions.
- The product should also have a precise application method that ensures accurate and even distribution of the active ingredients around the targeted areas.
- Results should be noticeable within a few hours, but may take longer to fully develop and peak in intensity.
- The effects of an at-home botox alternative typically last between 2-4 months, depending on individual factors such as skin type, muscle mass, and personal metabolism.
When it comes to safety, there are several concerns that should be taken into consideration when using an at-home botox alternative:
- Risks of adverse reactions, such as bruising, redness, swelling, and itchiness, can occur if the product is not used correctly or in excess.
- As with any skincare treatment, there is a risk of allergic reactions to certain ingredients, particularly those that are new to your skin.
- Individuals with pre-existing medical conditions, such as nerve damage or muscle disorders, should consult with a healthcare professional before using an at-home botox alternative.
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women may also want to exercise caution when using certain skincare products, especially those that contain active ingredients that have not been extensively tested for safety in these populations.
It’s also essential to look for a product that has undergone rigorous testing and clinical trials to ensure its efficacy and safety before it is released on the market.
- Certifications from reputable regulatory bodies, such as the FDA or EU’s Cosmetics Directive, can provide assurance that a product meets certain standards for safety and effectiveness.
- A transparent ingredient list and clear instructions for use can also help to alleviate concerns about potential risks or side effects.
- Ultimately, it’s crucial to weigh the benefits of an at-home botox alternative against the potential risks and consider individual circumstances before making a decision.
Botox injections are generally considered safe when administered by a qualified healthcare professional in a sterile environment. However, as with any medication or treatment, there can be side effects and risks associated with its use.
The FDA has reported several common side effects of Botox, including temporary redness, swelling, or bruising at the injection site. These side effects are usually mild and resolve on their own within a few days.
Temporary eyelid drooping (ptosis) is another possible side effect of Botox, although this is more likely to occur if the medication spreads beyond the targeted area. This can be temporary and may resolve on its own or with treatment from an eye doctor.
Drooling or difficulty swallowing can also occur in some individuals, particularly those who receive injections in areas that are close to these structures. These side effects are usually mild and short-lived, but in rare cases can persist for weeks or even months after treatment.
There have been reports of more serious side effects associated with Botox use, including eyelid spasms, facial pain, and difficulties with speech or swallowing. In rare cases, these complications can be life-threatening, and it is essential to seek immediate medical attention if they occur.
The FDA has also reported a small but significant risk of corneal exposure associated with Botox injections. This occurs when the medication causes the eyelid to droop, leading to exposure of the cornea (the clear layer on the front of the eye). In rare cases, this can lead to infection or damage to the cornea.
Another possible side effect is facial asymmetry, where one side of the face appears more affected than the other. This can be caused by the spread of Botox beyond the targeted area or by the use of multiple injection sites in different areas of the face.
The risk of infection from Botox injections is generally low if proper technique and sterilization protocols are followed. However, as with any invasive medical procedure, there is a small chance of infection or other complications.
Individuals who are pregnant, breastfeeding, or have certain underlying medical conditions may be at higher risk for adverse reactions to Botox. For example, those with neuromuscular disorders or myasthenia gravis should exercise caution when considering Botox treatment.
It is also essential to note that Botox can interact with other medications or worsen existing medical conditions. Individuals who are taking certain medications, such as blood thinners or immunosuppressants, should inform their healthcare provider before receiving Botox injections.
To minimize the risk of side effects and complications from Botox use, it is crucial to select a qualified healthcare professional with extensive experience in administering this medication. Additionally, following proper technique and using sterile equipment can help ensure safe and effective treatment.
By understanding the potential side effects and risks associated with Botox, individuals can make informed decisions about their medical care and take steps to minimize any adverse reactions.
Ultimately, Botox injections should only be performed by a qualified healthcare professional in a sterile environment. If you are considering Botox treatment, be sure to discuss your individual health risks and concerns with your doctor before proceeding.
Evaluating the effectiveness and safety of any cosmetic treatment, including products that mimic the effects of Botox, such as a “Botox in a bottle” solution, is crucial for potential users to make informed decisions.
One study published in the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology examined the rare but serious side effects associated with these types of treatments. The study highlighted that eyelid drooping or facial weakness can be among the more severe adverse reactions to these products.
The researchers noted that while many people may experience mild side effects, such as redness, swelling, or bruising at the injection site, there is a risk of more serious complications with certain ingredients or formulations.
Eyelid drooping, also known as ptosis, can be caused by the toxin used in these products affecting the nerve signals that control eyelid movement. Facial weakness can occur if the toxin affects the nerves controlling facial muscles.
Facial weakness can manifest in different ways, including difficulty closing the eyes or eyebrows, weakness of facial muscles, or an uneven smile.
It is essential for individuals considering using a “Botox in a bottle” solution to carefully weigh the potential benefits against the risks and to consult with a qualified healthcare professional before treatment.
A thorough examination and discussion of individual medical history, including any previous allergies or sensitivities, can help identify potential risks and ensure safe use of these products.
Regulatory agencies, such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), closely monitor cosmetic treatments for safety and efficacy, often requiring manufacturers to conduct extensive testing before approval for public sale.
Manufacturers must also adhere to established guidelines for labeling, packaging, and storage of these products to minimize the risk of adverse reactions.
In addition to regulatory oversight, it is essential for individuals using a “Botox in a bottle” solution to carefully follow instructions provided by the manufacturer and to report any unusual or concerning symptoms to their healthcare provider promptly.
A comprehensive understanding of both the potential benefits and risks associated with these treatments can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health and well-being.
Regulations and Guidelines
Botox is a highly regulated and scrutinized product, with strict guidelines and protocols in place to ensure its safe and effective use. One of the key factors that sets Botox apart from other cosmetic treatments is its comprehensive regulatory framework.
-
In the United States, Botox is regulated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as a prescription medication, rather than a cosmetic treatment. This means that it must be administered by a licensed healthcare professional, such as an MD or DO, in a clinical setting.
-
The FDA requires manufacturers of Botox to conduct rigorous testing and submit extensive documentation before it can be approved for use. This includes demonstrating its safety and efficacy in treating specific medical conditions, such as facial spasms and crossed eyes.
-
Botox is also subject to ongoing monitoring and evaluation by regulatory agencies. The FDA requires manufacturers to conduct regular post-marketing studies to assess the long-term safety and effectiveness of Botox.
The licensing and approval process for Botox is multifaceted, involving both federal and state-level regulations.
-
In the US, Botox must be licensed by the FDA before it can be marketed or sold. This involves submitting a New Drug Application (NDA) that includes detailed information on its composition, manufacturing process, and intended use.
-
Additionally, state medical boards require practitioners to complete specialized training and certification programs in order to administer Botox legally.
-
The American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS) also plays a significant role in regulating the use of Botox. The ASPS has established guidelines for its safe and effective use, which are based on scientific evidence and expert consensus.
Botox manufacturers must comply with strict quality control standards to ensure that their product meets regulatory requirements.
-
Manufacturers must adhere to Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines, which dictate how products are formulated, tested, and packaged.
-
Botox also undergoes rigorous testing for purity, potency, and sterility. This ensures that the product is free from contamination and meets the highest standards of quality.
-
Furthermore, manufacturers must conduct regular inspections and audits to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and industry standards.
The combination of strict regulations, rigorous testing, and ongoing monitoring helps to ensure that Botox is a safe and effective treatment option for cosmetic uses. This sets it apart from other cosmetic treatments, which may not be subject to the same level of scrutiny.
Botox has been a widely used cosmetic treatment for decades, but its popularity has led to an increased demand for a product that mimics its effects without undergoing medical training. One such product is a “botox in a bottle” or a facial serum infused with peptides and other active ingredients that claim to provide similar results.
However, the regulations surrounding these products vary by country and region. In the United States, for example, the FDA regulates cosmetic products, including those claiming to have anti-aging benefits.
- The FDA requires manufacturers of cosmetics, including facial serums, to undergo a pre-market review process before their product can be sold in the US market. This involves submitting documents and data to support the safety and efficacy of the product.
- Once approved, the product is then tested for safety and purity through clinical trials. These trials must demonstrate that the product does not cause adverse reactions or interact with other medications.
- The FDA also requires manufacturers to label their products accurately and truthfully, including any warnings or cautions related to use.
Guidelines for labeling and advertising these products are also in place. In the US, the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) regulates advertising claims, ensuring that they are substantiated by scientific evidence.
- The FTC requires advertisers to provide clear and concise information about their product’s ingredients, benefits, and risks.
- Advertisers must also support their claims with clinical data or other credible sources of information.
- Fines for non-compliance can be significant, up to $41,000 per violation in some cases.
In Europe, the European Union (EU) has its own set of regulations governing cosmetic products, including those claiming to have anti-aging benefits. The EU’s Cosmetics Directive sets standards for product safety, labeling, and advertising.
- The directive requires manufacturers to conduct toxicity tests on their products before they can be sold in the EU market.
- Manufacturers must also ensure that their products are properly labeled with information about ingredients, usage, and contraindications.
Despite these regulations and guidelines, there is still some gray area surrounding “botox in a bottle” products. While some may be genuinely effective at improving fine lines and wrinkles, others may contain low-quality or ineffective ingredients.
- Consumers should be cautious when selecting facial serums claiming to have anti-aging benefits, as the effectiveness of these products can vary widely depending on individual skin types and concerns.
- Look for products that are formulated with clinically proven peptides, such as acetyl hexapeptide-8 or palmitoyl pentapeptide-4.
In conclusion, while “botox in a bottle” products may offer promise, it’s essential to understand the regulations and guidelines surrounding these products. By being informed consumers, we can make more educated choices about which products are right for us and maximize their potential benefits.
Botox, a neurotoxin protein derived from _Clostridium botulinum_, is a widely used cosmetic treatment for facial wrinkles and fine lines. The FDA has licensed its use for cosmetic purposes in the United States.
The FDA regulates Botox through the Biologics Licensing Process, which involves rigorous testing and evaluation of the product’s safety and efficacy. To become a licensed treatment, Botox must meet strict standards set by the agency.
The FDA requires that Botox be manufactured in an _Environmental Protection Agency_-registered facility to ensure compliance with good manufacturing practice (GMP) guidelines.
Before being approved for cosmetic use, Botox undergoes a thorough review of its pharmacology, including studies on its mechanism of action and potential side effects.
The FDA also requires that Botox be administered by a trained healthcare professional who has completed a course in the safe use of the product. This is to minimize the risk of adverse reactions.
For cosmetic use, Botox is typically administered via an
The FDA has established guidelines for the safe and effective use of Botox for cosmetic purposes. These guidelines include recommendations for dosage, injection technique, and follow-up care.
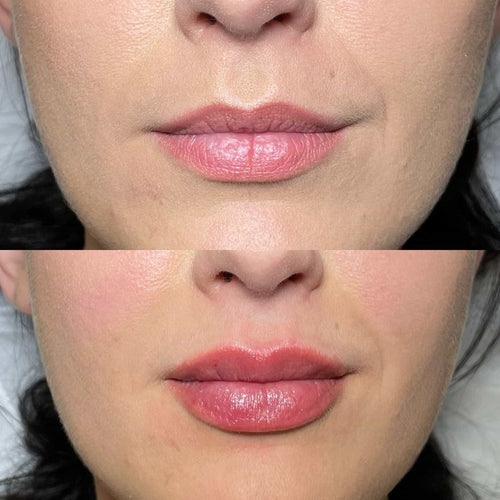
Additionally, the American Society of Dermatologic Surgery (ASDS) has developed its own set of best practice guidelines for using Botox in facial rejuvenation treatments.
The use of Botox for cosmetic purposes is also subject to certain state-specific regulations, which may vary depending on the jurisdiction.
In general, these regulations require that practitioners follow established protocols and guidelines when administering Botox, including proper training, informed consent, and post-treatment care.
The FDA and other regulatory agencies continue to monitor the safety and efficacy of Botox for cosmetic use, and update their guidelines and recommendations accordingly.
Botox has become a popular cosmetic treatment for wrinkles and fine lines, but it’s essential to understand the regulations and guidelines surrounding its use.
The American Academy of Dermatology recommends that patients consult with a qualified healthcare professional before undergoing Botox treatment in order to ensure their safety and optimal results.
A qualified healthcare professional is typically a *_board-certified dermatologist_* or a *_licensed physician_*, who has the necessary expertise and experience to administer Botox injections safely and effectively.
The Academy recommends that patients discuss the following with their healthcare professional before undergoing Botox treatment:
*Purpose of the treatment: What are you hoping to achieve with Botox treatment, and how will it address your specific concerns?
*Medical history: What medical conditions do you have, and what medications are you currently taking that may interact with Botox?
*Safety concerns: Are there any potential risks or side effects associated with Botox treatment that you should be aware of?
*Alternative options: Have you considered other treatments for your concerns, and what are their potential benefits and drawbacks?
The American Academy of Dermatology also emphasizes the importance of choosing a qualified and licensed *_medical spa_* or *_cosmetic clinic_* to administer Botox treatment.
A reputable medical spa or cosmetic clinic should have:
*a board-certified dermatologist or physician on staff: Who will be administering your treatment, and what is their expertise in Botox injections?
*Proper equipment and sanitation procedures: What measures are taken to ensure the cleanliness and sterility of the treatment area?
*a clear understanding of Botox dosing and administration: How will your treatment be customized to meet your individual needs, and what is the protocol for administering Botox?
By following these guidelines and regulations, patients can minimize their risk of complications and ensure a safe and effective Botox treatment experience.
Botox, a popular cosmetic treatment, has become increasingly accessible through various products on the market, claiming to replicate its effects without the need for injections. However, it’s essential to understand the regulations and guidelines surrounding these products to ensure safe use.
The FDA (Food and Drug Administration) regulates these products in the United States, considering them as cosmetics rather than medical devices. While this classification provides more flexibility for manufacturers, it also means that the standards for testing, labeling, and marketing are less stringent than those for prescription medications.
A key regulatory framework governing cosmetic products is the Federal Cosmetology Act of 1938, which prohibits the advertising of any cosmetics as “for preventing or curing” any disease. This act primarily focuses on protecting consumers from deceptive advertising rather than ensuring the safety of individual products.
The FDA’s Cosmetic Ingredient Review (CIR) program evaluates the safety of ingredients used in cosmetic products. The CIR examines a substance’s history, scientific understanding of its effects on human health, and any existing data on its safe use. While this process provides valuable guidance, it is not a formal approval process for individual products.
Another critical aspect of regulation concerns labeling and packaging requirements. Cosmetic labels must display specific information, such as the ingredients used, net weight, and any warnings or cautions. Manufacturers are also responsible for ensuring that their products meet relevant standards for quality control and safety testing.
The European Union (EU) regulates cosmetic products differently, with a focus on ensuring their safety and efficacy through pre-market approval. EU regulations require manufacturers to conduct clinical trials and obtain authorization before marketing their products. While this approach provides more comprehensive oversight, it can make it more challenging for small companies or new product developers to enter the market.
A crucial aspect of understanding regulations is recognizing that individual products may not be regulated in the same way as Botox injections themselves. Botox injections are FDA-approved and subject to strict guidelines, whereas cosmetic products claiming similar effects may not require the same level of scrutiny.
It’s also worth noting that some regulatory agencies have raised concerns about the lack of transparency in labeling for certain “at-home” treatments or devices mimicking Botox. Manufacturers often downplay the risks associated with these products, leaving consumers unaware of potential side effects or interactions with other health conditions.
To ensure safe use and minimize adverse reactions, it’s essential to follow instructions carefully when using these products. Users should be aware of any allergies or sensitivities they may have, as well as any medications or treatments they are currently undergoing.
Ultimately, regulations governing Botox-like products in a bottle serve as an added layer of protection for consumers. By understanding the differences between FDA-approved injections and at-home treatments, users can make informed choices about their health and beauty needs.
It’s also worth mentioning that some states have introduced laws regulating the sale and marketing of these products, which can affect how they are offered to customers. For example, in California, manufacturers must provide specific information on product labels regarding “red flag warnings” for products that may cause eye irritation or other serious reactions.
Moreover, regulatory agencies like the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) have expressed concerns about the misuse of Botox in cosmetic treatments, particularly among younger individuals. As a result, some manufacturers have begun to develop more targeted treatments for specific areas of concern, such as facial wrinkles or eyelid spasms.
As regulations evolve, so too do consumer expectations and awareness regarding safety and efficacy. Manufacturers must adapt their marketing strategies and labeling practices to ensure transparency and compliance with regulatory requirements.
The increasing popularity of Botox-like products has also sparked debate about the long-term effects and potential risks associated with repeated use. Regulatory agencies are continually monitoring these issues, updating guidelines, and conducting further research to address concerns and promote safe practices.
Regulations and guidelines play a crucial role in ensuring safety and quality in various industries, including the cosmetics and pharmaceutical sectors. When it comes to products like those mentioned in “What Is Like Botox In A Bottle?”, adherence to established regulations is essential to protect consumers from potential harm.
In many countries, regulatory bodies such as the FDA (Food and Drug Administration) in the United States, the EMA (European Medicines Agency), and Health Canada, among others, set guidelines for the development, manufacturing, testing, and distribution of cosmetics and pharmaceuticals. These regulations often include requirements for labeling, packaging, and instructions for use.
Industry standards such as Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) also ensure that products are manufactured in a safe and controlled environment, minimizing the risk of contamination or adulteration. GMP encompasses principles such as proper cleaning and sanitation procedures, quality control measures, and record-keeping protocols.
Beyond regulatory compliance, many industries have adopted best practices to enhance product safety and efficacy. For instance, in the case of injectable treatments like Botox, healthcare professionals follow guidelines set by organizations such as the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS) and the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD). These guidelines outline recommended dosages, administration techniques, and contraindications for various patient populations.
Furthermore, many companies in the cosmetics and pharmaceutical industries adhere to voluntary standards such as those set by the National Science Foundation (NSF) or the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). These standards focus on product quality, sustainability, and environmental responsibility.
In addition to these industry-wide guidelines, manufacturers themselves often develop their own quality control procedures to ensure consistent product performance. This may include testing protocols for efficacy and safety, as well as regular audits to verify compliance with regulatory requirements.
Consequently, the interplay between regulations, industry standards, and best practices contributes significantly to ensuring the safety and quality of products like those mentioned in “What Is Like Botox In A Bottle?”. While regulatory bodies set the foundation for these efforts, it is ultimately the collective responsibility of manufacturers, healthcare professionals, and consumers to adhere to established guidelines and best practices to guarantee optimal outcomes.
Botox has become a widely recognized and sought-after cosmetic treatment for temporary muscle relaxation and wrinkle reduction. However, many individuals are curious about the process and what it entails, particularly when compared to other popular injectable treatments like fillers and neurotoxins.
One of the primary ways to distinguish Botox from other injectables is through regulations and guidelines that govern their use. In the United States, for example, the FDA regulates the manufacturing, quality control, and labeling of all cosmetic products, including Botox.
The FDA has established specific guidelines for the safe and effective use of Botox, which includes requirements for manufacturer certifications, labeling, and storage. Additionally, there are strict regulations governing the training and qualifications of healthcare professionals who administer Botox injections.
To ensure compliance with these regulations, manufacturers like Allergan, the producer of Botox, must adhere to Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) standards, which dictate aspects such as quality control measures, equipment maintenance, and packaging procedures. This rigorous quality control process helps guarantee that Botox meets high safety and efficacy standards.
Similarly, healthcare professionals who administer Botox injections are required to follow established guidelines and protocols for preparation, administration, and post-treatment care. These guidelines cover topics such as patient selection criteria, dosage calculations, and potential side effects management.
In terms of regulations, the FDA has designated Botox as a Class III device, which requires premarket approval before being marketed in the United States. This classification indicates that Botox poses significant risks if not used properly and that it must undergo rigorous testing for safety and efficacy before being cleared for commercial use.
Beyond federal regulations, many states and local governments also have their own laws and guidelines governing the use of Botox and other injectable treatments. For example, some jurisdictions may require registration with state boards or professional associations to administer certain types of cosmetic procedures, including Botox injections.
Furthermore, professional organizations like the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery (ASDS) and the American Academy of Facial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (AAFPRS) provide guidelines and recommendations for healthcare professionals who wish to administer Botox or other injectable treatments. These organizations often develop and disseminate evidence-based protocols that help standardize best practices and minimize risks.
In the context of popular treatments like fillers, neurotoxins, and chemical peels, regulations and guidelines play a crucial role in ensuring public safety and protecting consumers from potential harm. By establishing clear standards for product development, training, and use, regulatory agencies and professional organizations help maintain confidence in the cosmetic industry and promote responsible innovation.
Ultimately, the complex interplay between regulations and guidelines influences every step of the Botox journey, from initial consultation to final result. While Botox may be marketed as a convenient, at-home treatment option, its safe and effective use requires adherence to these established protocols, which prioritize both patient safety and the integrity of the cosmetic treatment process.
The American Society for Dermatologic Surgery (ASDS) establishes guidelines for safe and effective use of Botox to ensure that patients receive proper treatment and minimize potential side effects.
These guidelines cover various aspects of Botox administration, including
-
The indication and contraindication of using Botox for different cosmetic purposes, such as facial wrinkles and frown lines.
-
The proper dosage and frequency of administration to achieve optimal results while minimizing the risk of side effects.
-
The selection of appropriate patient candidates based on factors such as age, health status, and medical history.
-
The use of Botox in combination with other treatments, such as fillers or surgery, to enhance aesthetic results.
-
The importance of maintaining a clean and sterile environment during treatment to prevent infection and promote healing.
-
The need for thorough patient education on the risks and benefits of Botox treatment, as well as proper post-treatment care and follow-up.
In addition to these guidelines, the ASDS also provides recommendations for safe and effective use of Botox in various situations, such as
-
Pregnancy and breastfeeding: The potential risks and benefits of using Botox during pregnancy and breastfeeding are not well established, and its use is generally avoided until further research is conducted.
-
Children and adolescents: The safety and efficacy of using Botox in minors have not been thoroughly studied, and it is not recommended for this age group without further clinical trials.
-
Pacemakers and other implantable devices: Botox may interact with certain medical implants, such as pacemakers, and should be used with caution or avoided altogether in these situations.
By following these guidelines and recommendations, healthcare professionals can ensure that patients receive safe and effective treatment with Botox, and minimize the risk of adverse reactions and complications.
Botox, a popular cosmetic treatment, has become increasingly common over the years. However, with its widespread use comes the need for regulations and guidelines to ensure safe and effective administration.
A study published in the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology highlights the importance of adhering to best practices when using Botox. The researchers found that strict adherence to protocols can significantly reduce the risks associated with this treatment, such as facial asymmetry, eyelid drooping, and corneal exposure.
According to the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery (ASDS), Botox is administered in a sterile environment, typically using a micro-needling device or a specialized cannula. This minimizes the risk of infection and ensures accurate placement of the toxin.
The study also emphasizes the importance of proper patient selection, as certain medical conditions, such as eye disorders, muscle spasms, or neuromuscular diseases, may increase the risk of adverse reactions to Botox treatment. Patients must be thoroughly evaluated and informed about potential risks before undergoing the procedure.
Furthermore, pre-treatment assessments are crucial in determining the ideal dosage and administration technique for each patient. A thorough understanding of facial anatomy and muscle function is necessary to avoid over- or under-dosing, which can lead to suboptimal results or increased risk of complications.
The researchers also noted that post-treatment care plays a vital role in ensuring successful outcomes. Patients must be advised on how to manage potential side effects, such as bruising, swelling, or dry eyes, and instructed on how to minimize these risks.
Adequate training and experience are essential for medical professionals administering Botox treatment. A well-qualified practitioner is better equipped to recognize potential complications and take corrective action if necessary.
In addition to these factors, continued education and research are vital in staying up-to-date with the latest developments and advancements in Botox technology. The medical community must continually evaluate and refine treatment protocols to ensure the highest standards of care.
The study’s findings emphasize the importance of collaboration and communication between healthcare providers, patients, and industry professionals. By working together, we can minimize risks associated with Botox treatment and ensure that patients receive the best possible outcomes.
In conclusion, adherence to regulations and guidelines is crucial in ensuring safe and effective Botox treatment. By following established protocols, selecting suitable patients, administering accurate dosages, providing thorough post-treatment care, and maintaining ongoing education, we can minimize risks and optimize results for our patients.
Read more about Hopeless Book here. Read more about Critic Forever here. Read more about Dejour Magazine here. Read more about Melissa J Design here.
- How to Navigate Relationships When Your Partner Identifies as Demigender - September 8, 2025
- Gaslighting and emotional manipulation how to protect your mental health - September 8, 2025
- Understanding Polyamorous Parenting and Its Unique Challenges - September 8, 2025



